What is dyslexia?
Dyslexia is a specific learning difficulty (SpLD) affecting the ability to read, write, and spell. It is a different way of processing language with no bearing on intelligence. Early recognition and understanding of dyslexia can make a huge difference by opening doors to support and strategies that empower dyslexic people to flourish. In this blog, we’ll be assessing dsylexia. We’ll explore what dyslexia is, why testing for it matters, and how to take the first steps toward understanding if a formal assessment is right for you.
The effects of dyslexia
Dyslexia is a neurodevelopmental condition that affects how the brain processes language. It often impacts abilities like:
- Phonological processing: Recognising and working with the sounds in words.
- Decoding: Accurately breaking down words while reading.
- Reading fluency: Reading smoothly and understanding text.
- Spelling: Forming words correctly and consistently.
- Written expression: Communicating ideas effectively in writing.
It’s important to remember that dyslexia isn’t linked to intelligence. Many dyslexic people excel in creativity, problem-solving, and big-picture thinking. These skills bring diverse perspectives and value.
Assessing dyslexia with a diagnostic assessment
A dyslexia diagnostic assessment is a comprehensive process led by qualified specialists including educational psychologists and trained specialist assessors. These assessments may vary slightly for each individual, but typically include the following steps:
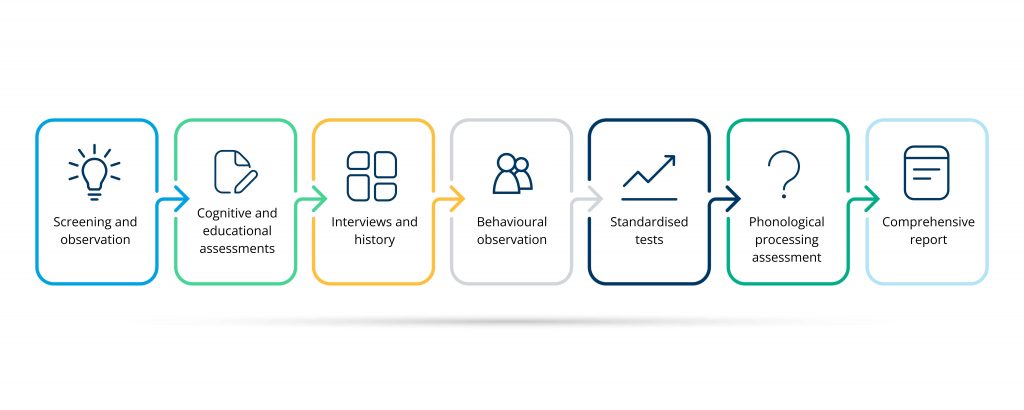
- Screening and observation: The process starts with a screening to look for signs of dyslexia, including challenges with reading, writing, and phonological awareness (recognising and working with sounds in words).
- Cognitive and educational assessments: These tests evaluate skills like reading fluency, comprehension, spelling, working memory, and phonological processing. The goal when assessing dsylexia is to understand where difficulties lie and where strengths shine.
- Interviews and history: Gathering insights from the individual, their parents or guardians and teachers help provide a full picture. This might include developmental milestones, family history, and educational experiences.
- Behavioural observation: During the assessment, the assessor will observe responses to tasks, noting any signs of frustration, avoidance, or anxiety that may stem from difficulties with reading or writing.
- Standardised tests: Standardised assessments compare the individual’s abilities to what’s typical for their age group, helping to identify specific gaps or challenges that suggest dyslexia.
- Phonological processing assessment: Since dyslexia often involves difficulty processing sounds, assessments focus on phonological awareness, memory, and manipulation.
- Comprehensive report: After completing the tests, the specialist provides a detailed report. This document includes the assessment results, a diagnosis (if appropriate), and tailored recommendations for support, strategies, and accommodations at school or work.
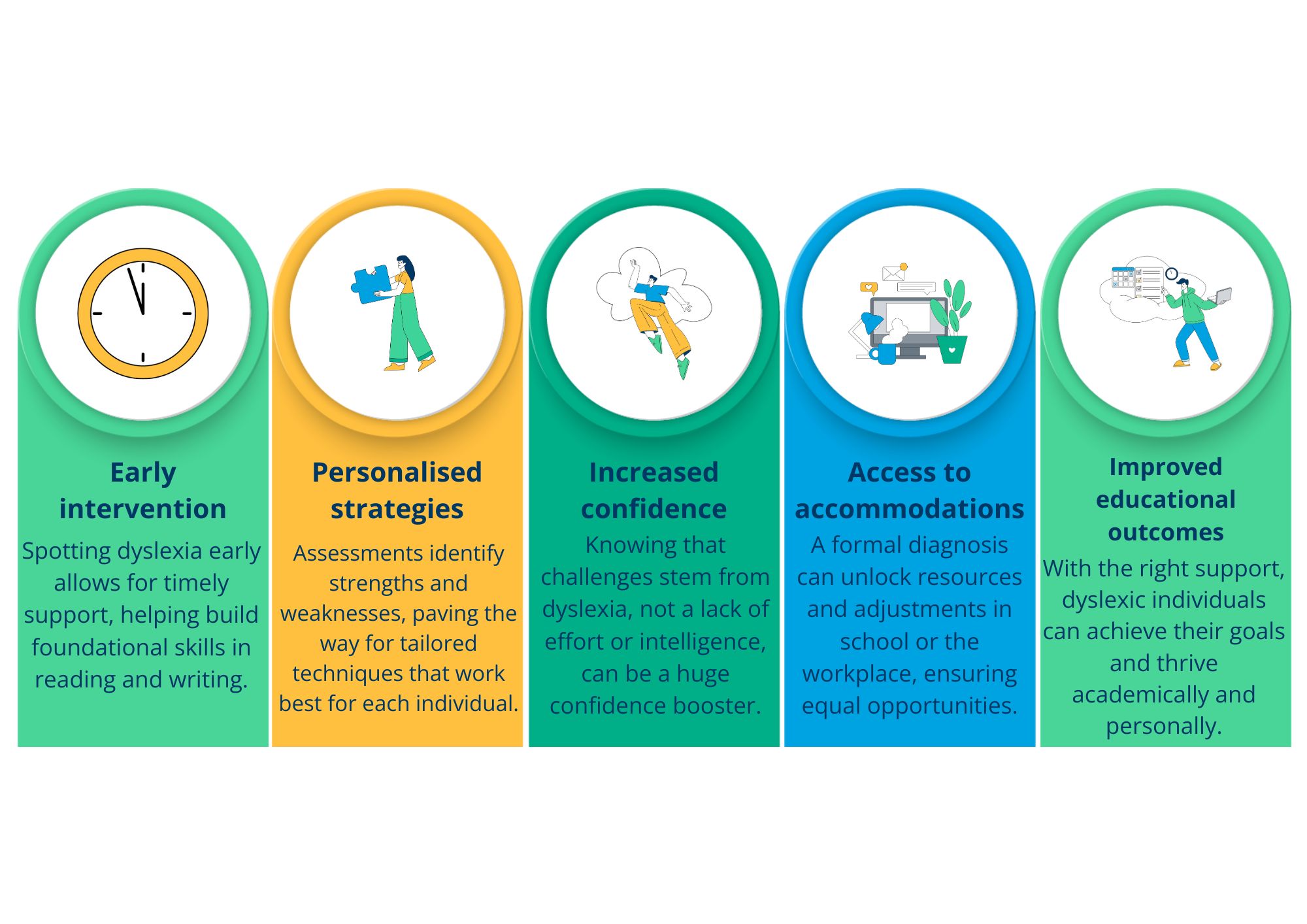
The benefits of assessing dyslexia
Understanding and diagnosing dyslexia can have life-changing benefits, no matter your age:
Assessing dyslexia at Aim Forward
If you or your child shows signs of dyslexia, getting a formal assessment can be life-changing. We specialise in providing thorough dyslexia assessments that offer clear insights and practical recommendations, helping dyslexic individuals unlock their full potential.
We offer online or in-person diagnostic assessments for dyslexia.
Get in touch to book an assessment or chat with one of our team.


Recent Comments